
Reproduction Of Protists And Bacteria by vsk3234
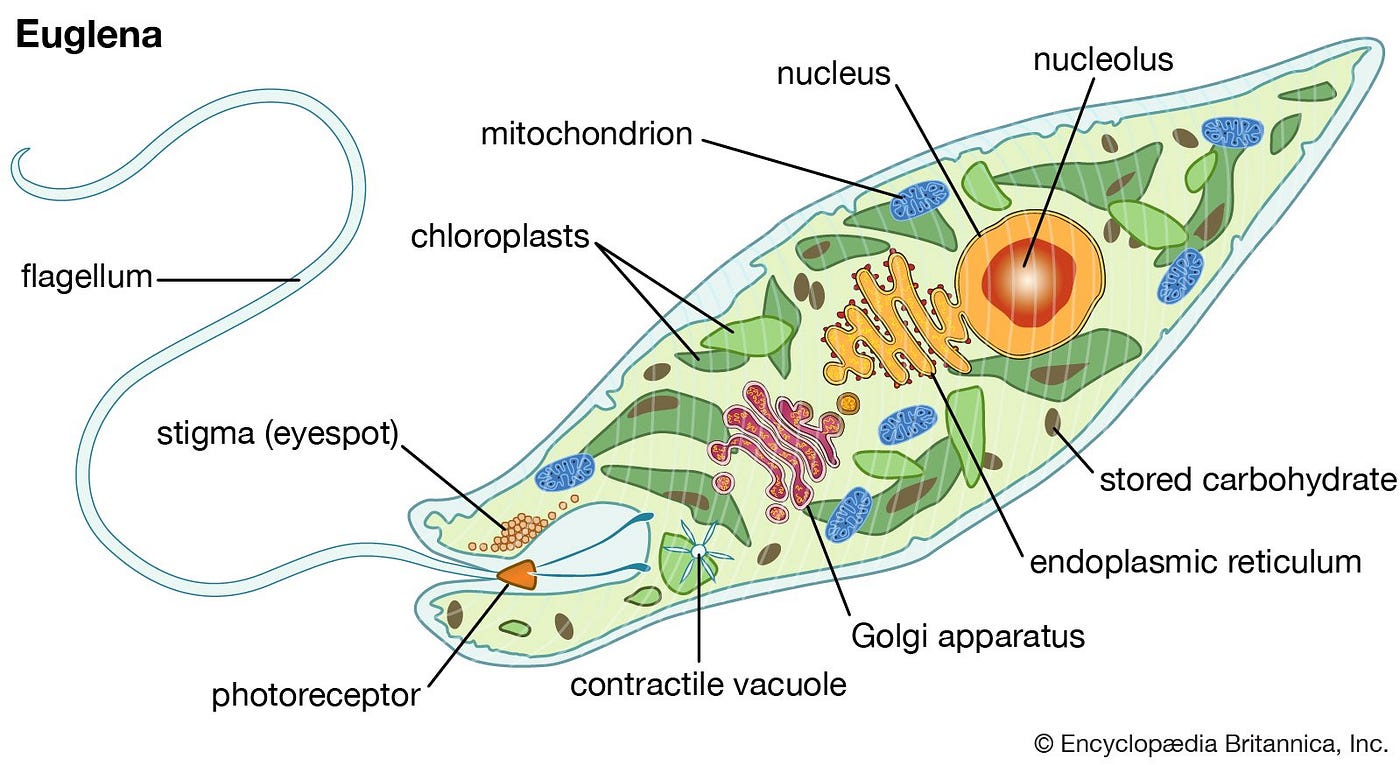
protist, any member of a group of diverse eukaryotic, predominantly unicellular microscopic organisms. They may share certain morphological and physiological characteristics with animals or plants or both.

Unicellular Eukaryotic Parasites · Microbiology
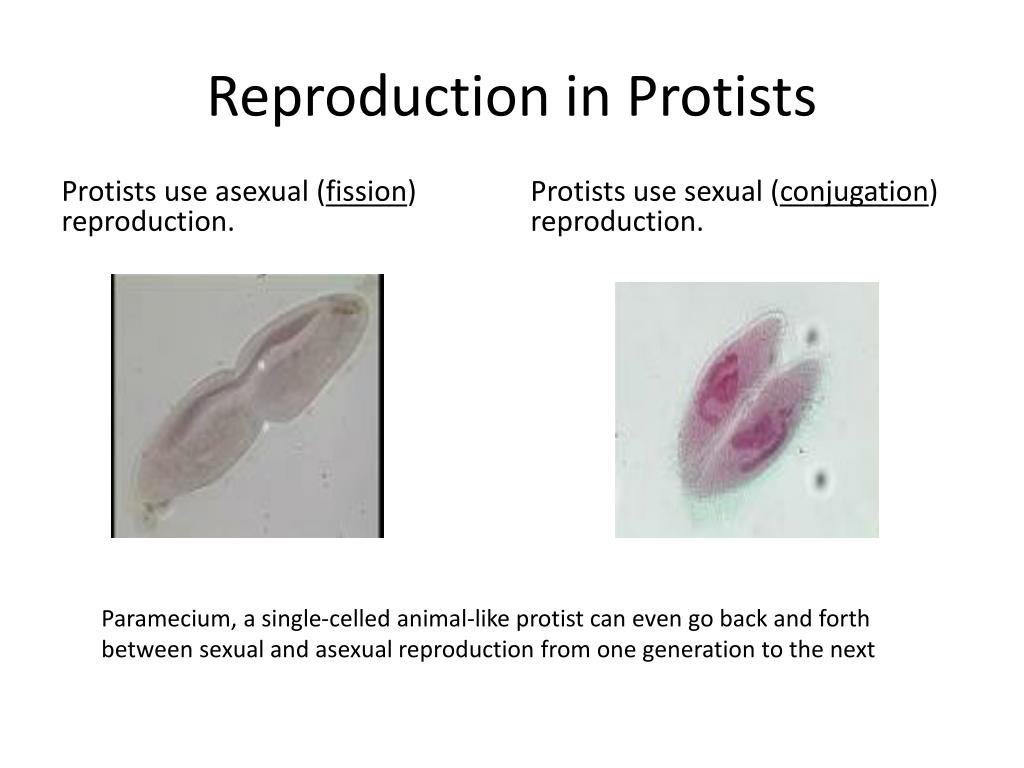
How do protists grow and reproduce? Some protists reproduce through binary fission, which produces two daughter cells identical to the parent cell. The daughter cells then grow by.

Protist Reproduction Diagram Quizlet
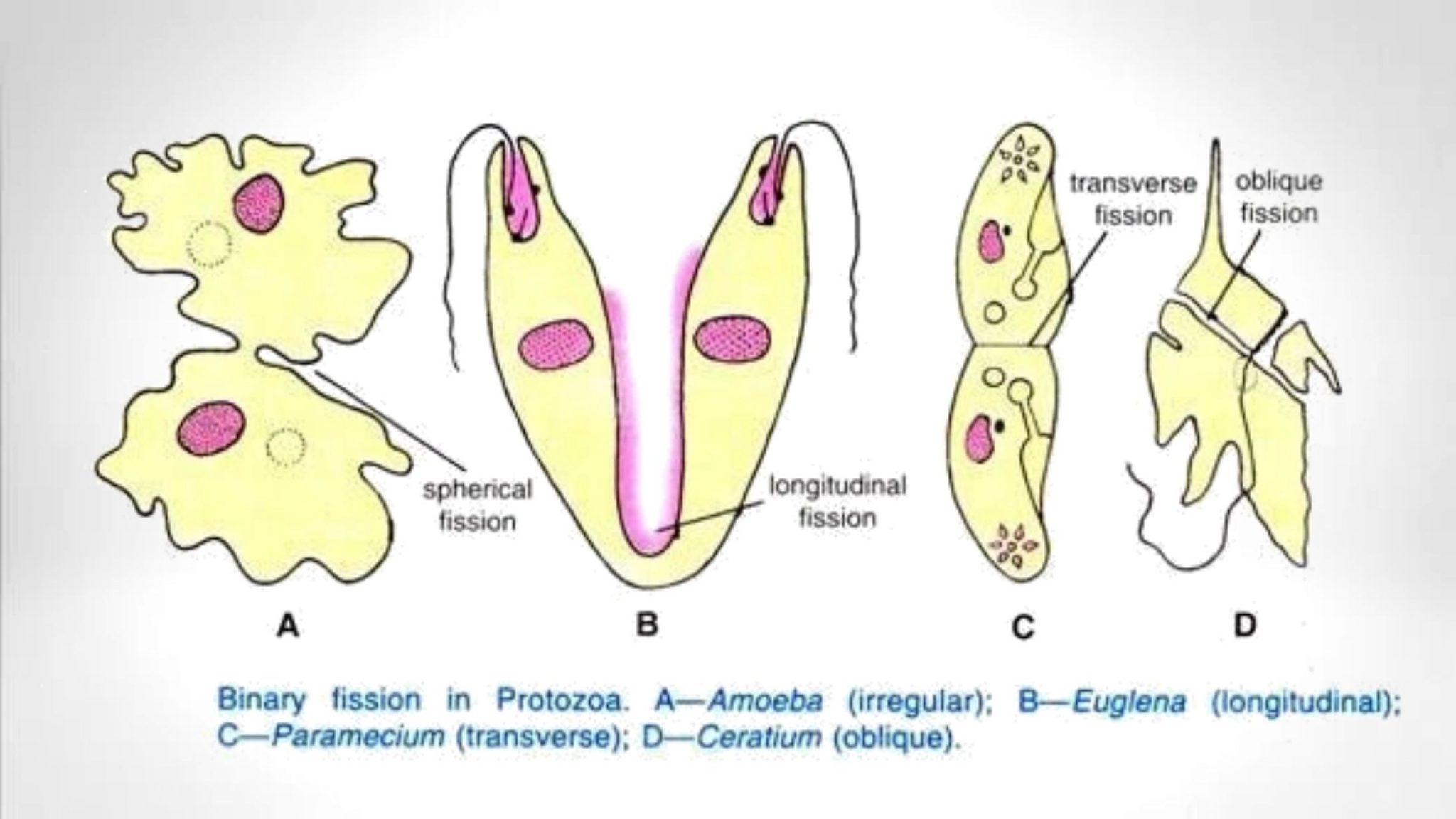
Protists reproduce by many mechanisms. Most undergo some form of asexual reproduction, such as binary fission, to produce two daughter cells. In protists, binary fission can occur along the transverse or longitudinal axis of the cell, depending on the axis of orientation.. Protists do not create food sources only for sea-dwelling organisms.
PPT Unit 2 Notes Kingdom Protista PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2300074
However, sexual reproduction when it does occur, can take on varied forms, whether self-fertilized or through cross-fertilization. For example, Plasmodium, the causative agent for malaria, has an asexual as well as a sexual phase in its life cycle. Many protists are also believed to show facultative sexual reproduction. Types of Protists

Groups of Protists Biology I
Protists reproduce by a variety of mechanisms. Most undergo some form of asexual reproduction, such as binary fission, to produce two daughter cells. In protists, binary fission can be divided into transverse or longitudinal, depending on the axis of orientation; sometimes Paramecium exhibits this method. Some protists such as the true slime.
Reproduction In Protozoa Sexual Reproduction, Asexual Reproduction
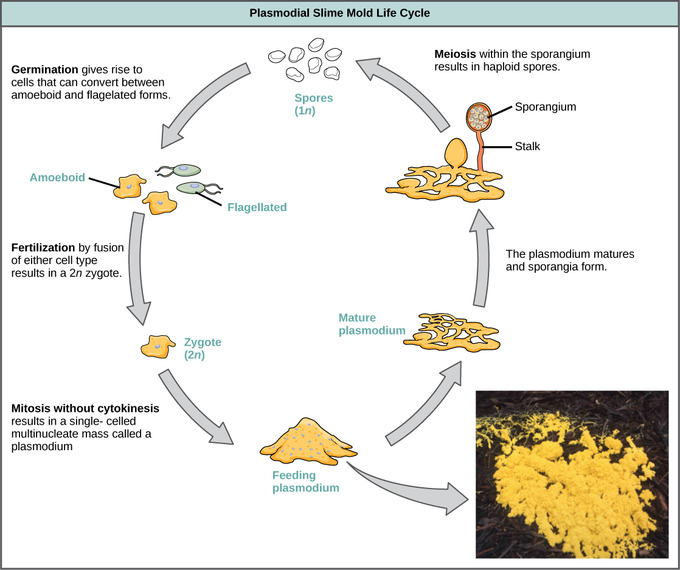
Life Cycles. Protists reproduce by a variety of mechanisms. Most undergo some form of asexual reproduction, such as binary fission, to produce two daughter cells.In protists, binary fission can be divided into transverse or longitudinal, depending on the axis of orientation; sometimes Paramecium exhibits this method. Some protists such as the true slime molds exhibit multiple fission and.
KINGDOM PROTOCTISTA (UNICELLULAR EUKARYOTES) by Biology Experts Notes Medium
How Do Protists Reproduce? ••• Updated July 08, 2019 By Lindsey Taylor Protists are organisms in the Kingdom Protista. They are usually microscopic and made up of only one protist cell, which means that they are unicellular.
.PNG)
Kingdom Protista part I Presentation Biology
Reproduction of Protists. Protists have complex lifecycles which are very different from other eukaryotes, such as humans. The green algae, Spirogyra, shown in Figure below, can reproduce both sexually and asexually.Other protists also go through cycles of sexual or asexual reproduction, depending on their species or sometimes their environmental conditions.
.PNG)
Kingdom Protista part I Presentation Biology
In this review we will discuss about origin of sex and different strategies of evolve sexual reproduction in some protists such that cause human diseases like malaria, toxoplasmosis, sleeping sickness, Chagas disease, and leishmaniasis. Keywords: Protists, Trypanosoma cruzi, sexual reproduction, meiosis genes.

How do most protists reproduce?
How do Protists Reproduce - Key takeaways. Protists are diverse organisms that reproduce both sexually and asexually. Asexual reproduction limits genetic diversity and can make a population susceptible to extinction from changing environmental conditions or diseases, hence some protists also reproduce sexually to introduce genetic variation.
Characteristics of Protists Boundless Biology
It usually exists as haploid cells that reproduce by binary fission. In a stressful environment, such as one that is very dry, Spirogyra may produce tough spores that can withstand harsh conditions. Spores are reproductive cells produced by protists and various other organisms. If two protist spores are close together, they can fuse to form a.

PPT Protists (Chapter 29) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2391888
7 Protists Protists, or Protista, historically encompassed all eukaryotic organisms that were neither animals, plants, or fungi. Modern studies have clearly demonstrated that Protista in their traditional sense were an artificial group, including a number of independent evolutionary lineages.

Types of Protist Reproduction Video & Lesson Transcript
How does a protist reproduce? A protist reproduces in two ways. The first reproduction method is asexual reproduction, where the protist replicates itself without the aid of another.

Groups of Protists Biology for Majors II
Life Cycles. Protists reproduce by a variety of mechanisms. Most undergo some form of asexual reproduction, such as binary fission, to produce two daughter cells. In protists, binary fission can be divided into transverse or longitudinal, depending on the axis of orientation; sometimes Paramecium exhibit this method.

Groups of Protists OpenStax Biology
Sexual reproduction may allow the protist to recombine genes and produce new variations of progeny that may be better suited to surviving in the new environment. However, sexual reproduction is often associated with resistant cysts that are a protective, resting stage. Depending on their habitat, the cysts may be particularly resistant to.

How Do Protists Reproduce? Sciencing
Reproduction. Protists reproduce by a variety of mechanisms. Most are capable some form of asexual reproduction, such as binary fission to produce two daughter cells, or multiple fission to divide simultaneously into many daughter cells. Others produce tiny buds that go on to divide and grow to the size of the parental protist.