
Electrical Engineering World Transformer Parts Electrical engineering books, Power
612 Pages by CRC Press Description In the newest edition, the reader will learn the basics of transformer design, starting from fundamental principles and ending with advanced model simulations.

Transformer design part I YouTube
Basic Transformer Theory The above figure represents the essential elements for a transformer: a magnetic core with a primary and secondary coil wound on the limbs of the magnetic core. An alternating voltage (Vp) applied to the primary creates an alternating current (Ip) through the primary.
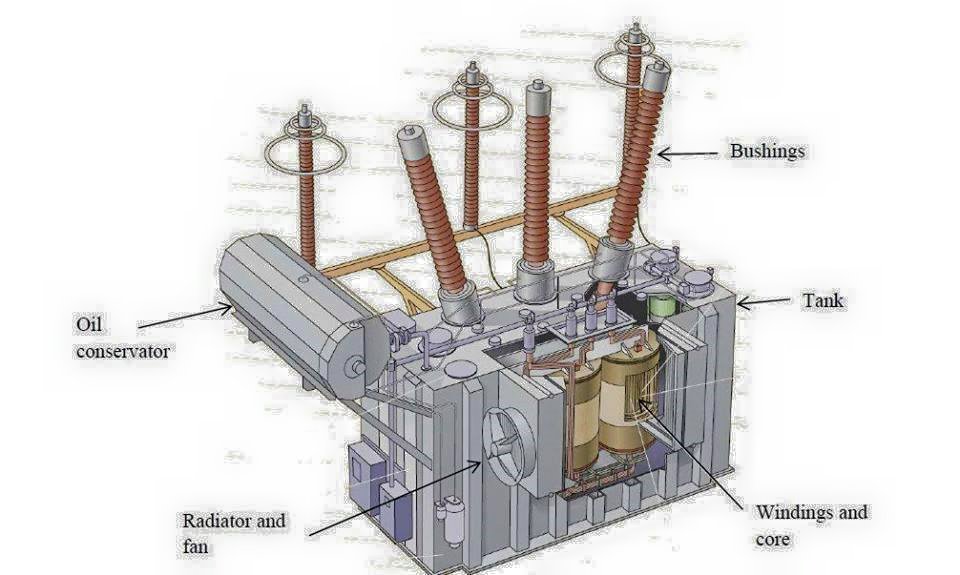
Power Transformer Showing Electrical Engineering Books
Basics of Transformer Published February 22, 2018 0 E Emmanuel Odunlade Author TRANSFORMERS Transformers generally, are devices capable of converting quantities from one value to the other.
Current Transformer Design Software Free Download
April 9, 2023 by Andrew Strohm A transformer transfers power from one circuit to another without any change in frequency. There are two types of windings in a transformer, one is primary winding and the other is secondary winding.

SI TRX172SL12ATLNANANAUNA 172" Wall Projector Screen Slate AT 1.2 Projector Screen Store
First Online: 15 July 2020 18k Accesses Abstract In the design methods of the previous chapter, copper loss P cu and maximum flux density B max are specified, while core loss P fe is not specifically addressed.

Transformer Theory of Operation Inst Tools
Connect one probe at one end of one of the wires and the other probe to the opposite end of the same wire. The resistance should be very low. Repeat for the second wire. Step 6: If either resistance measurements from steps 4 or 5 indicate a problem, the winding (s) must be re-made. Step 7: Power the primary winding of the transformer (you can.

Power Transformers Design and Application PEguru
Basic guidelines for specifying and selecting small single-phase transformers Determine the required secondary output power. The process of transformer design starts with determining how much power will be needed at the secondary winding of the transformer. And this can be calculated by multiplying the required maximum secondary voltage level.
Dynamic Tonality
Fundamentals of transformer design By H du Preez, Consultant A transformer is a static piece of equipment with a complicated electromagnetic circuit. The electrical energy is transferred from one electrical circuit to another through a magnetic field. In its simplest form, a transformer consists of two conducting coils having a mutual inductance.

Transformer Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
Power Transformer Design This Section covers the design of power trans-formers used in buck-derived topologies: forward converter, bridge, half-bridge, and full-wave center-tap. Flyback transformers (actually coupled induc-tors) are covered in a later Section. For more spe-cialized applications, the principles discussed herein will generally.

Transformer Design, 230 V to 12 V Step Down Transformer, Materials
1 Overview Transformer Design Transformer Types Construction and Parts Core & Coils Electrical design Losses & Impedance Thermal, Dielectric & Short Circuit Cooling & Sound Level Mechanical design Tank Oil Preservation Transformer Manufacturing Process Power Transmission & Distribution
transformer concept 01 by nobody00000000 on DeviantArt
Design of core Rectangular core: It is used for core type distribution transformer and small power transformer for moderate and low voltages and shell type transformers. In core type transformer the ratio of depth to width of core varies between 1.4 to 2. In shell type transformer width of central limb is 2 to 3 times the depth of core.

Transformer Design, 230 V to 12 V Step Down Transformer, Materials
1 Power transformer design 1.1 Initial calculations 1.2 Type of iron (electrical steel) 1.3 Secondary turns calculation 1.4 Thickness of coil windings 1.5 Insulation 2 Wire selection 3 The core stack 3.1 Stacking Factor 3.2 Scrapless Laminations 3.3 Core Stack Assembly 4 Watts versus volt-amperes 5 Rectifier transformers 6 Equations
Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing Notes Enable BASIC transformer in DataStage
A basic transformer consists of two coils that are electrically separate and inductive, but are magnetically linked through a path of reluctance. The working principle of the transformer can be understood from the figure below. Transformer Working As shown above the electrical transformer has primary and secondary windings.

multiple choice questions on transformer 14 Electrical Engineering
A transformer basically is very simple static (or stationary) electro-magnetic passive electrical device that works on the principle of Faraday's law of induction by converting electrical energy from one value to another.

Transformer Design by RobertAtkins on DeviantArt
For example, if this transformer happens to have an impedance of 5.5%, it means the secondary (output) voltage will sag 5.5% below 24 VAC at full load, assuming the primary voltage is maintained at the standard 120 VAC level. 5.5% of 24 volts is 1.32 volts, and so this transformer's secondary voltage will "sag" from 24 volts down to 22.68.
Transformers 3 designs
Power Transformer Design Step No. 2 Calculate the electrical conditions, Ke Kf = 4.44, [sine wave] Ke = 0.145(4.44)2 (47 )2 (1.6)2 (lO 4) * =1.62 Step No. 3 Calculate the core geometry, Kg. *•-•£? [cm'] ^=31.7, [cm5] Step No. 4 Select a lamination from Chapter 3, comparable in core geometry, Kg.