
Entamoeba Histolytica & Amoebic Dysentery Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Amebiasis is a disease caused by a one-celled parasite called Entamoeba histolytica. Who is at risk for amebiasis? Although anyone can have this disease, it is more common in people who live in tropical areas with poor sanitary conditions. In the United States, amebiasis is most common in:

Traveling Small with a Nucleus Organism Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica, the etiological agent of amebiasis, is a major parasitic cause of morbidity and death, particularly in developing countries. It is estimated that around 50 million symptomatic cases and 100,000 deaths worldwide/year. [ 1]
Big Ben Entamoeba histolytica
Entamoeba histolytica is a protozoan that causes intestinal amebiasis as well as extraintestinal manifestations. Although 90 percent of E. histolytica infections are asymptomatic, nearly 50 million people become symptomatic, with about 100,000 deaths yearly. [1] Amebic infections are more prevalent in countries with lower socioeconomic conditions.

Entamoeba Histolytica Stepwards
If antibodies to E. histolytica are found, they are measured in units called titers. This is what your test results may mean: A titer less than 1:32 means you probably do not have amebiasis. A titer greater than 1:128 may mean an active or recent amebiasis infection. A titer between 1:256 and 1:2048 likely means a current and active amebiasis.
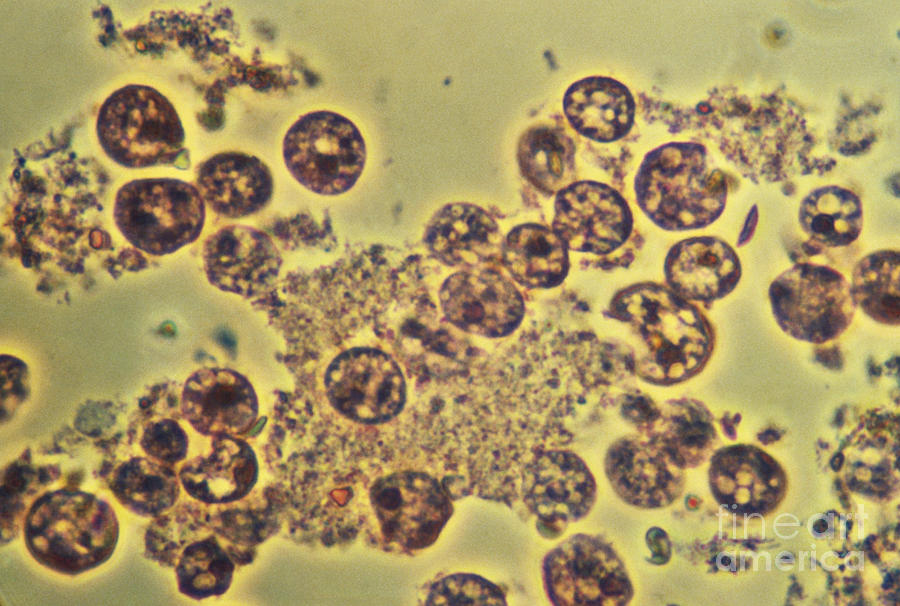
Entamoeba Histolytica Lm Photograph by Eric V. Grave
Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic amoebozoan, part of the genus Entamoeba. [1] Predominantly infecting humans and other primates causing amoebiasis, E. histolytica is estimated to infect about 35-50 million people worldwide. [1] E. histolytica infection is estimated to kill more than 55,000 people each year. [2]

trophozoite with centric endsome and crisp nuclear membrane 1000x
Entamoeba histolytica is an enteric protozoan parasite with worldwide distribution. It is responsible for amoebic dysentery (bloody diarrhea) and invasive extraintestinal amebiasis (such as liver abscess, peritonitis, and pleuropulmonary abscess).
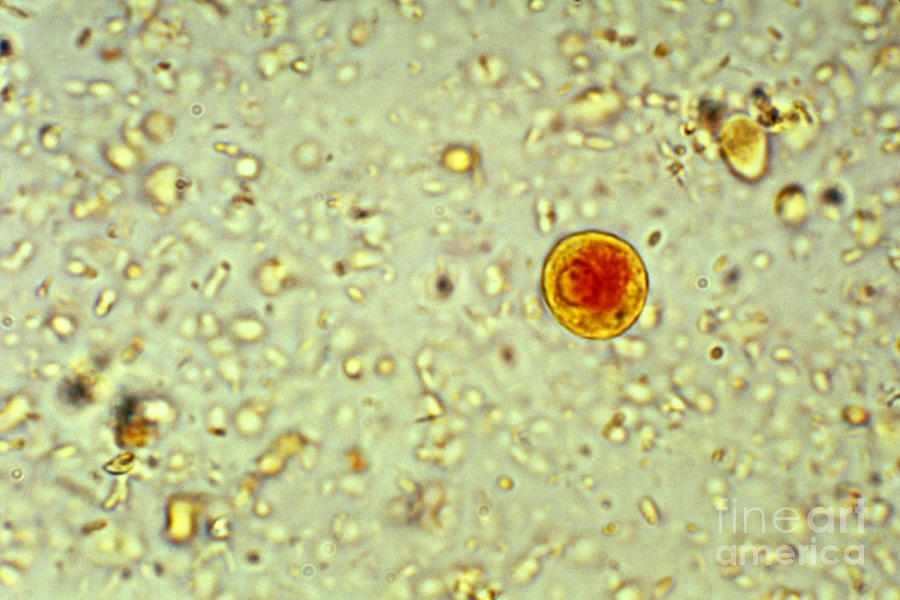
Entamoeba Histolytica Cyst 1 Photograph by Science Source Fine Art
Entamoeba histolytica is a unicellular, protozoon parasite of humans. It moves by a jelly-like tongue-like protrusion of the cytoplasm "pseudopodium.". In fresh-stool examined under the microscope, the trophozoite moves actively by a finger-like protrusion of the ectoplasm "pseudopodium," into which the cytoplasm is pulled moving the.
Blastocystis Parasite Blog microscopy
Diagnosis is by identifying E. histolytica in stool specimens and confirmed with immunoassays-detecting antigen in the stool, or by serologic tests if extraintestinal disease is suspected. Treatment for symptomatic disease is with metronidazole or tinidazole followed by paromomycin or another drug active against cysts in the lumen of the colon.

Entamoeba histolytica Microscope Slides
Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic parasitic protozoan that infects the digestive tract of predominantly humans and other primates. It is a parasite that infects an estimated 50 million people around the world and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries. Analysis of the genome allows new insight into the.

Public Domain Picture Entamoeba histolytica cyst. ID
Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites observed under the microscope stain with methylene blue (Observe that the cells did not accept the stain since they were still alive at the time the picture was.

Entamoeba histolytica (trophozoite) Motility progressive
Microscopic identification of cysts and trophozoites in the stool is the common method for diagnosing E. histolytica. This can be accomplished using: Fresh stool: wet mounts and permanently stained preparations (e.g., trichrome).

Parasitology Entamoeba coli? Entamoeba histolytica, Medical
Definition / general. Disease caused by infection of the large intestine with the protozoan parasite, Entamoeba histolytica. Several protozoan species in the genus Entamoeba colonize humans but not all of them are associated with amebiasis ( Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Amebiasis [Accessed 13 October 2023] )

Figure 1 from ASPECTS ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA Semantic Scholar
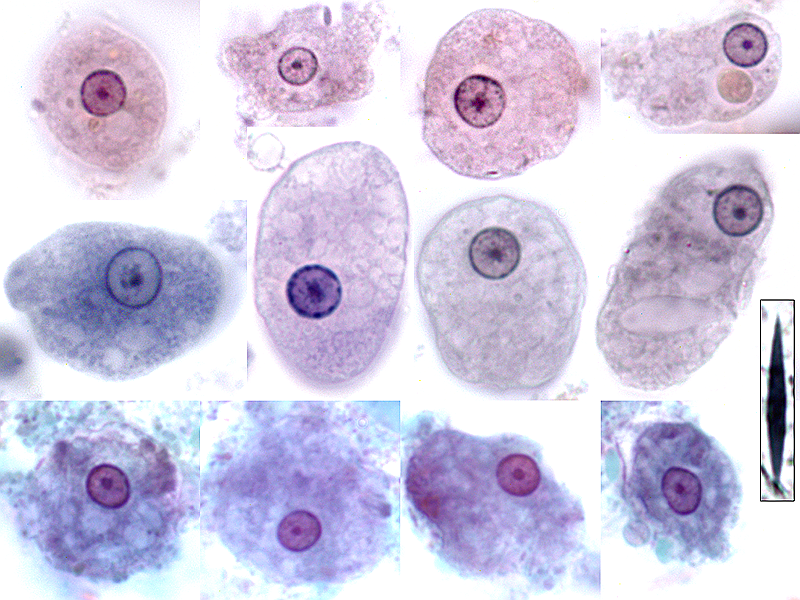
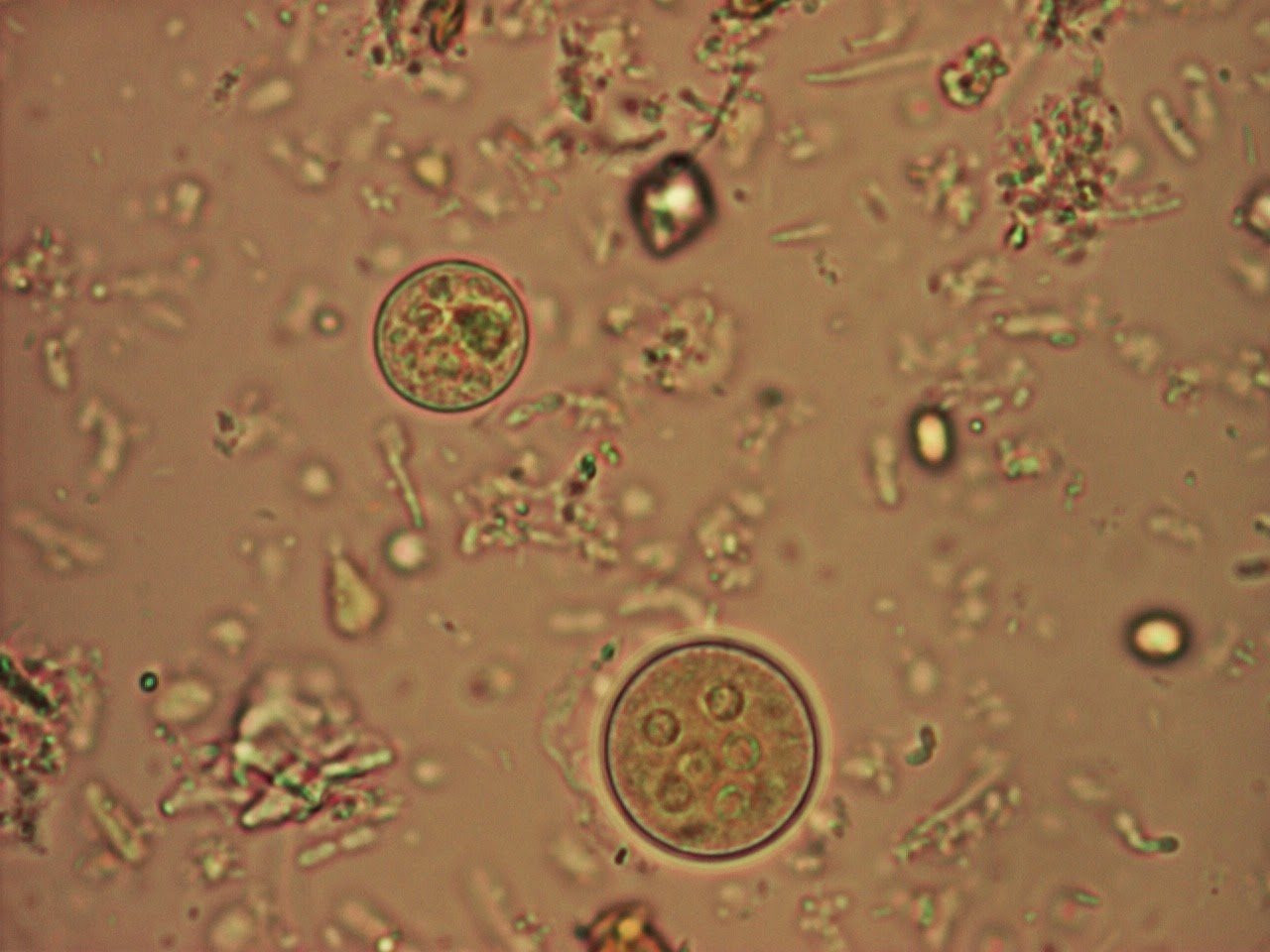
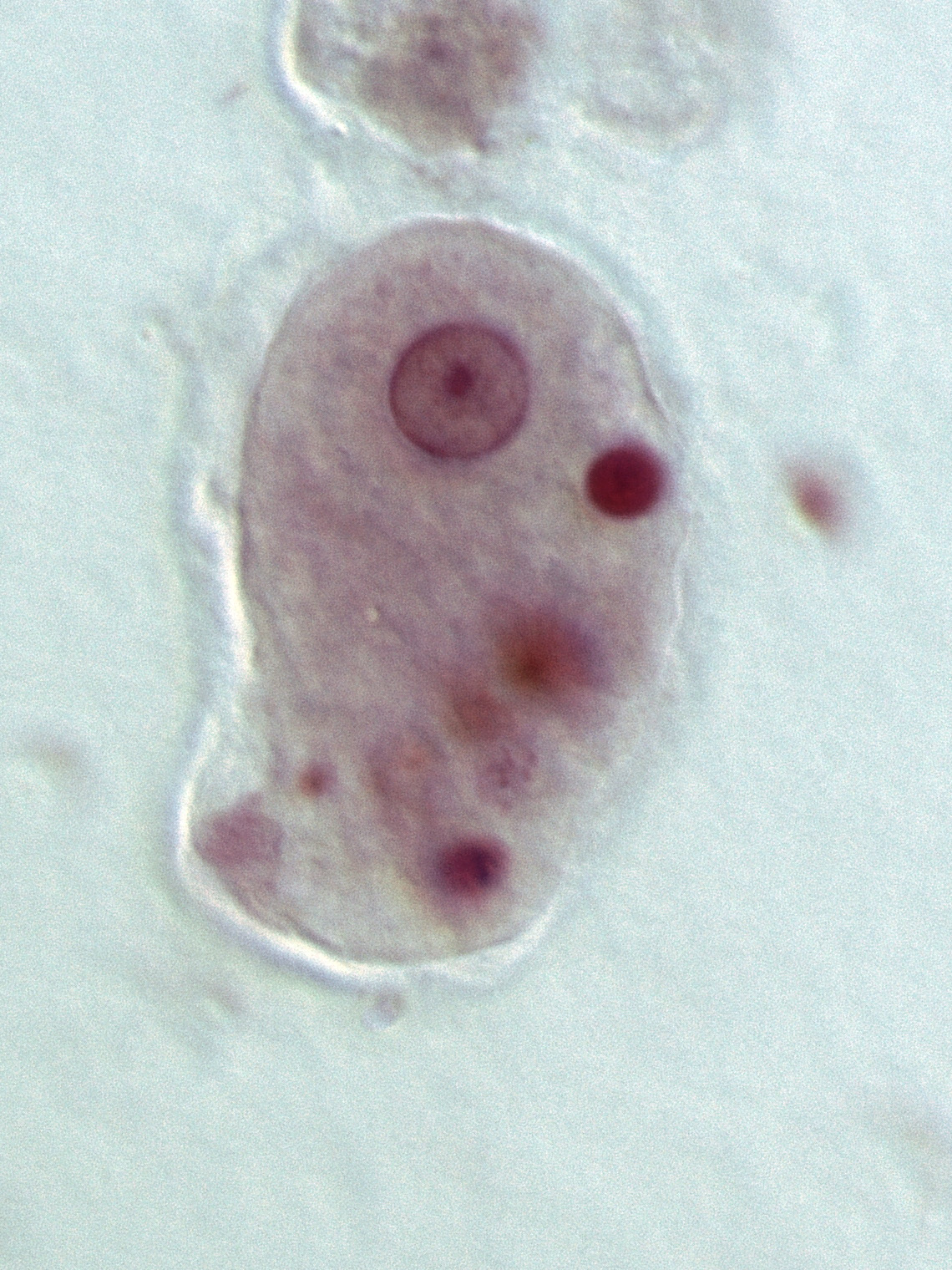
1. Wet mount Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar are morphologically identical species. In bright-field microscopy, E. histolytica/E. dispar cysts are spherical and usually measure 12 to 15 μm (range may be 10 to 20 μm). A mature cyst has 4 nuclei while an immature cyst may contain only 1 to 3 nuclei.

Entamoeba histolytica Trofozoites, Smear Microscope Slide
Classically, detection of Entamoeba histolytica is performed by microscopic examination for characteristic cysts and/or trophozoites in fecal preparations. Differentiation of E. histolytica cysts and those of nonpathogenic amoebic species is made on the basis of the appearance and the size of the cysts.
Parasites Tales of Humanity's Most Guests Mysteries of
Entamoeba Histolytica: Biology and Host Immunity. Hayley Gorman, Kris Chadee, in Encyclopedia of Microbiology (Fourth Edition), 2019. Abstract. Entamoeba histolytica is an intestinal dwelling parasite in the human gastrointestinal tract that causes diseases such as amebiasis, amebic colitis and amebic liver abscesses. In most cases, E. histolytica colonizes the host's gut without causing.
Entamoeba histolytica SaludBio
INTRODUCTION The genus Entamoeba contains many species, six of which ( Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar, Entamoeba moshkovskii, Entamoeba polecki, Entamoeba coli and Entamoeba hartmanni) reside in the human intestinal lumen.