
Глубокие мышцы, внутренние органы собаки Dog Muscles & Internal
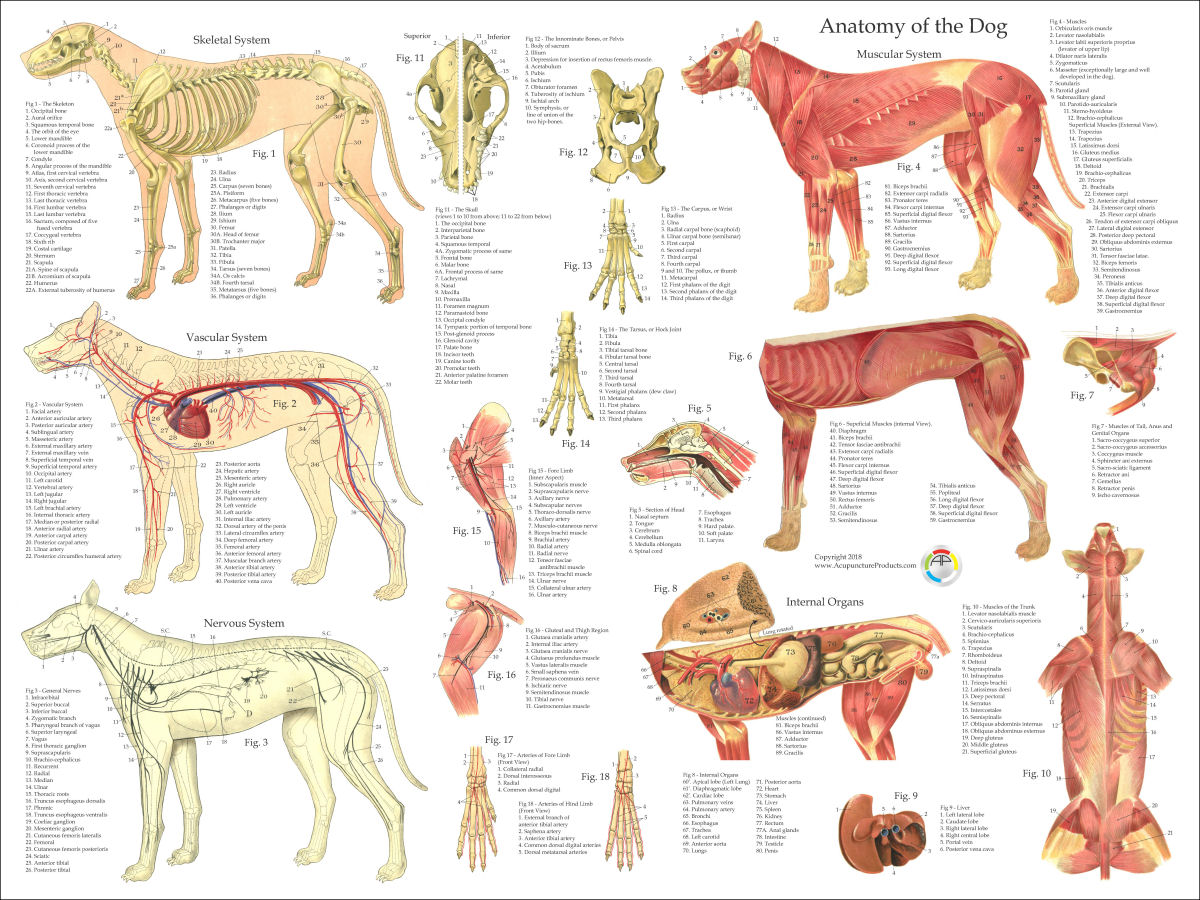
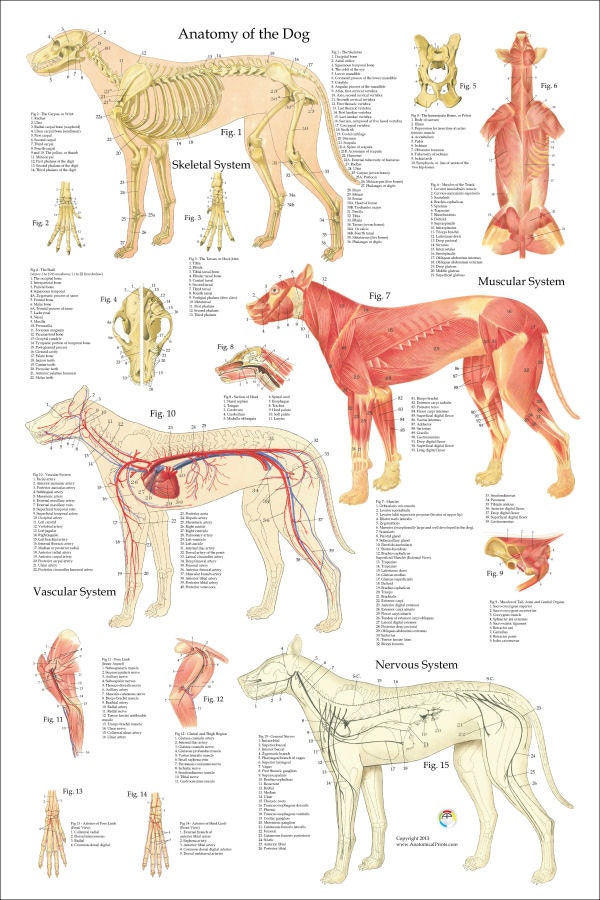
Anatomy atlas of the canine general anatomy: fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the dog (skeleton, bones, muscles, joints, viscera, respiratory system, cardiovascular system). Positional and directional terms, general terminology and anatomical orientation are also illustrated.

Anatomy of a male dog crosssection, showing the skeleton and internal
Whereas giant breeds can take between 18 months and 2 years for their growth plates to fuse. Speaking of skeletons, a dog has 320 bones in their body (depending on the length of their tail) and around 700 muscles. Muscles attach to bones via tendons. Depending on the breed of dog, they will have different types of muscle fibers.
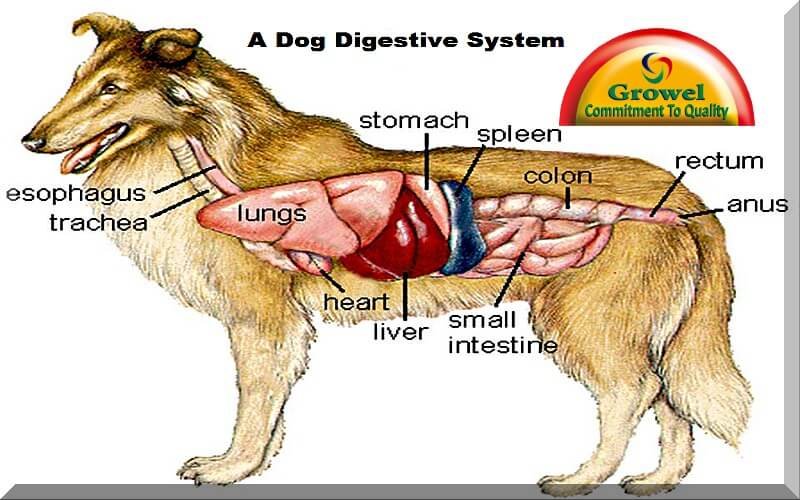
How is a Dog Digestive System Functioning? Growel Agrovet Private Limited
2021 Ultimate Guide to Dog Anatomy. As the pace of veterinary advancement accelerates, even the most experienced veterinary teams are challenged to keep up with all the changes that impact their practice. Veterinary teams need practical, concise and relevant visual aids at their fingertips while in practice, helping them to prescribe the right.

Dog Anatomy Stomach Anatomical Charts & Posters
The canine tibia is the major bone in the crus. The triangular proximal tibia is wider than the distal cylindrical tibia. Medial and lateral tibial condyles, an intercondylar eminence, and a tibial tuberosity are on the proximal tibia. The tibial plateau slopes distally from cranial to caudal.
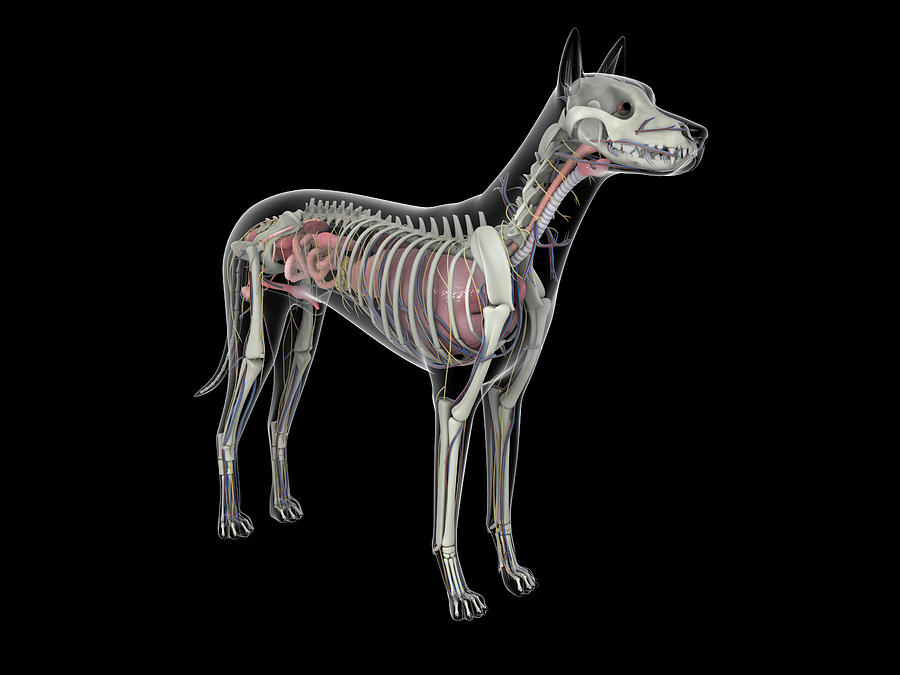
Dog Anatomy With Internal Organs Photograph by Stocktrek Images Fine
The complexity of dog internal anatomy ensures seamless function and survival. Understanding the dog internal anatomy is crucial. Here are the key components of the internal anatomy of the female dog's body: Nervous System. The nervous system is at the heart of every dog's interaction with the world. This intricate network of the brain.

A4 Veterinary Poster u00 Internal Organs Of The Dog (Animal Anatomy
It provides information about a dog's skeletal, reproductive, internal, and external anatomy, along with accompanying labeled diagrams. After mating, dogs experience something called a copulatory tie, wherein they remain in the coital position. The male dog dismounts the female at this time. The dogs can remain in this position from a few.

Pin em Anatomy
Anatomy of the thorax of the dog on CT:: Mediastinal vessels, Aortic arch, Mediastinum, Heart, Pulmonary arteries, Pulmonary veins. Thorax of the dog: cross-sectional anatomy on Computed Tomography (CT): Lungs, Trachea, Bronchi. Vertebral column - CT (Labrador): Thoracic vertebrae, Vertebral body, Pedicle of vertebral arch, Spinous process.
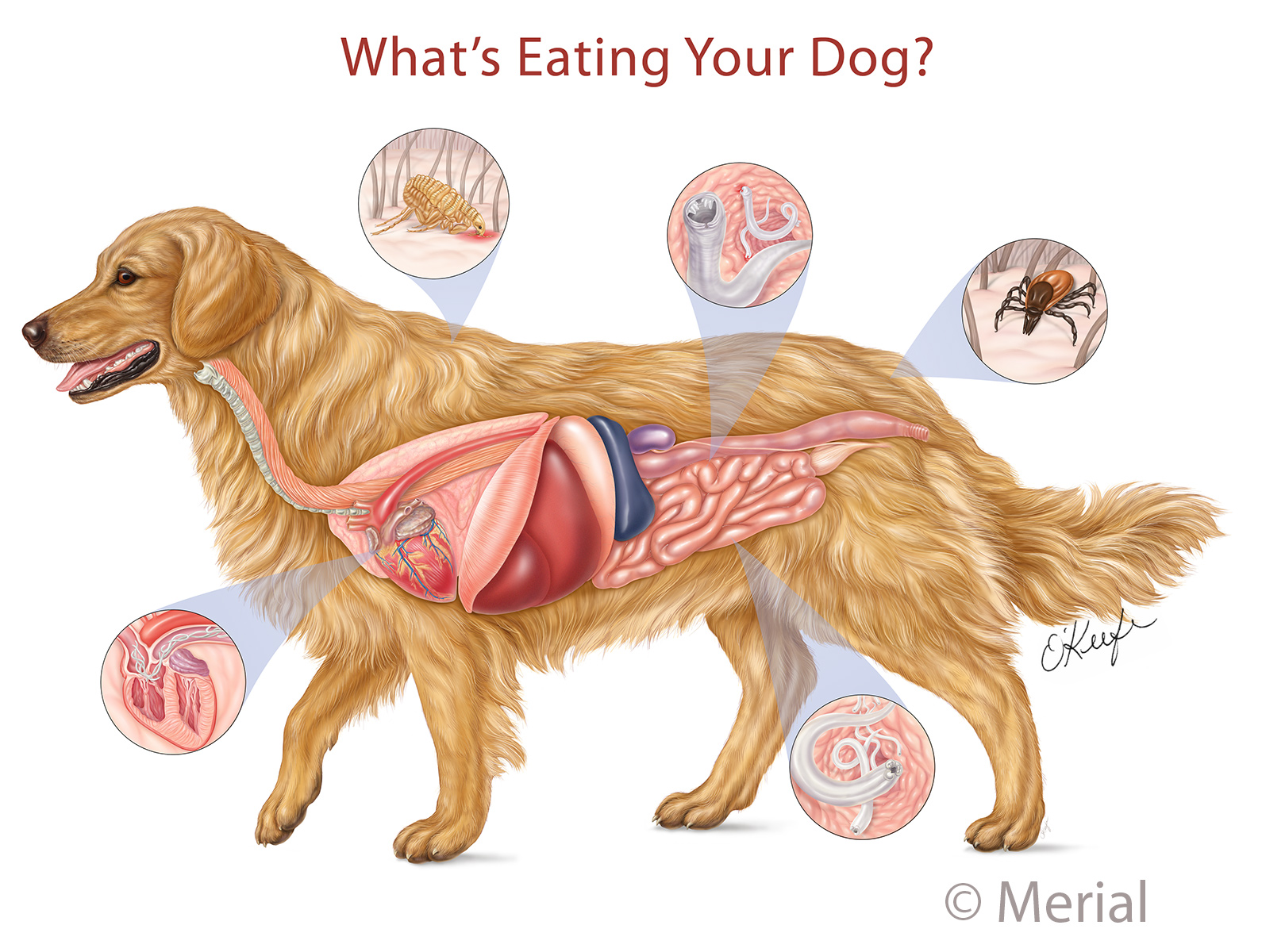
Dog Internal Anatomy Anatomical Charts & Posters
The spleen is another clinically important organ in dog internal anatomy. There is a roughly human foot-print-shaped structure spleen present in a dog. The ventral end is wider than the dorsal end of the dog's spleen. Again, the dog's spleen location is variable except for the upper end, which is below the proximal end of the last rib.
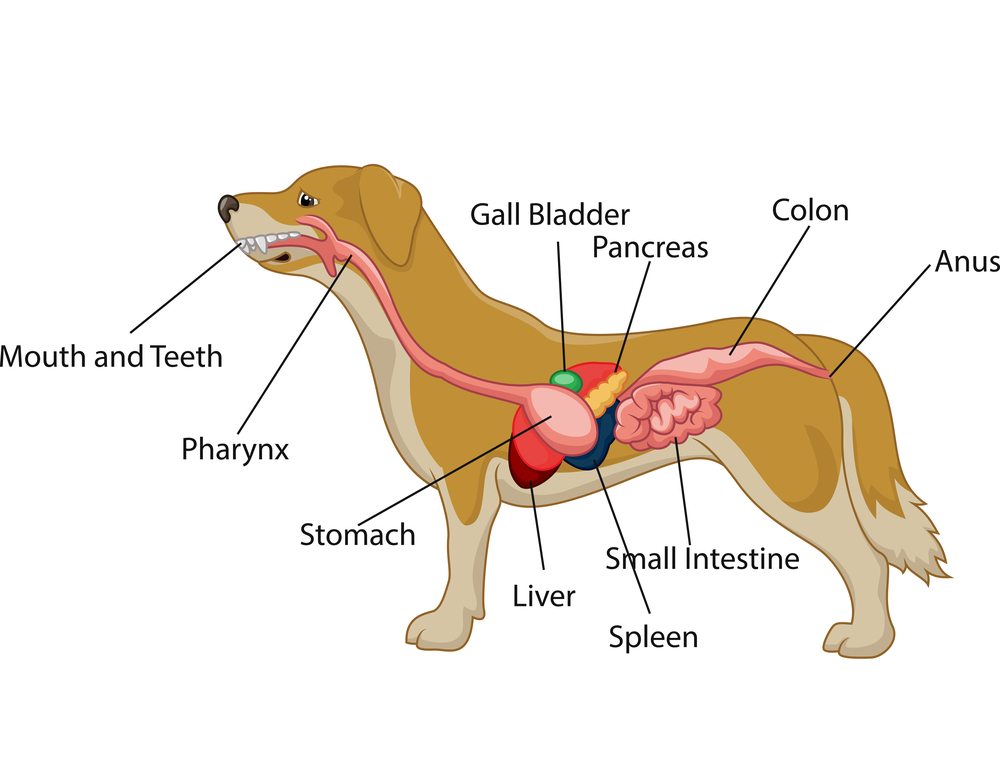
Dog Digestive Process and what the stages are and how it works
This detailed canine internal anatomy wall chart has been laminated for easy cleaning and to enable wipeable marker pens to be used for notation. This is one of our bestselling veterinary charts in the canine anatomy series, which includes the canine muscular system and canine skeletal anatomy charts. Designed and printed in the UK. Size: 50 x.
Dog Anatomy Poster
A dog's physical anatomy is designed to help them navigate their environment and perform various tasks. Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. One of the most important parts of a dog's anatomy is their skeleton.
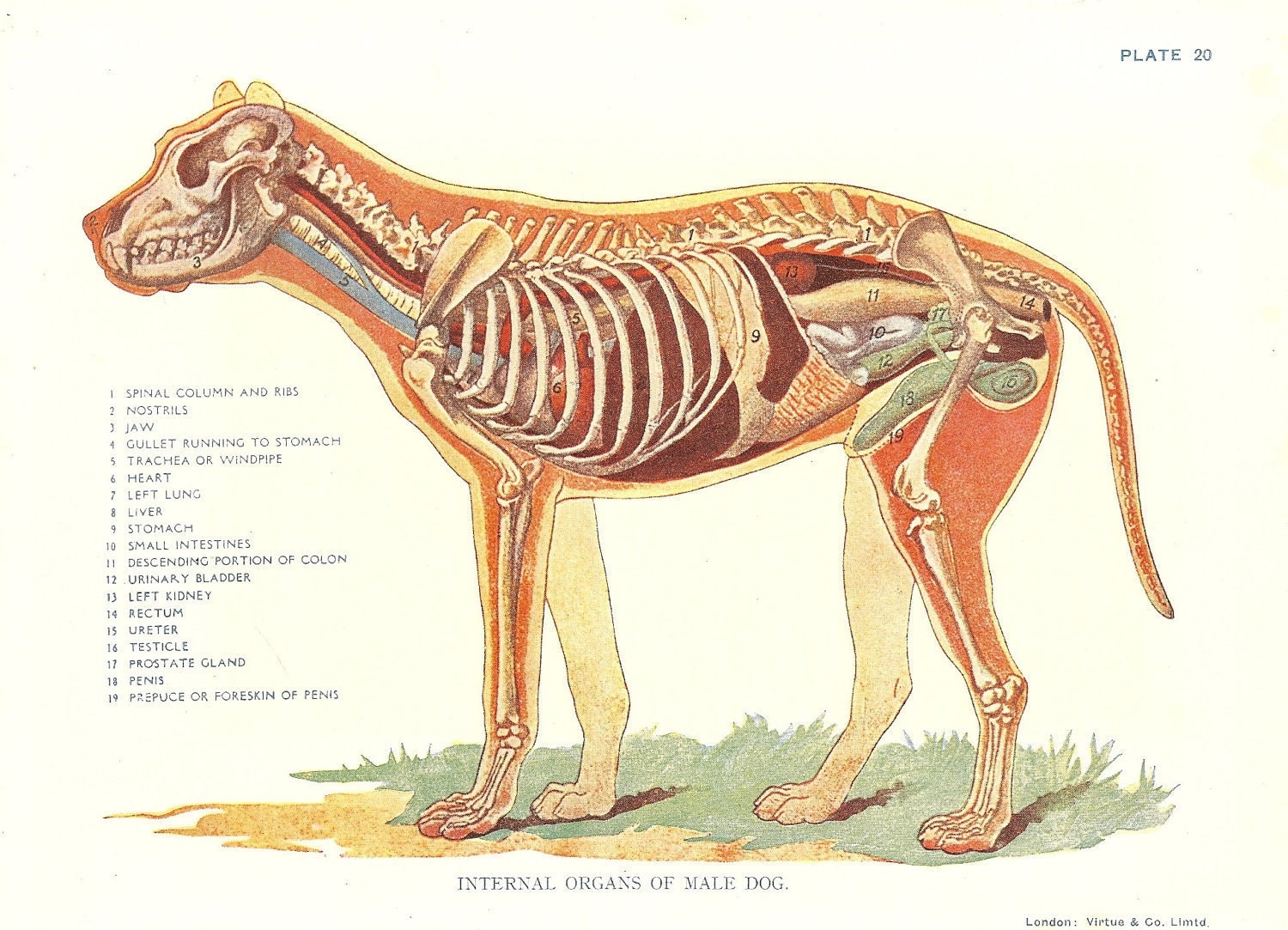
Dog Veterinary Print 1920s Internal Organs Of Male Dog
The internal anatomy of dogs, is very similar to the anatomy of other carnivorous mammals such as the cat. Dogs have a well-developed brain which is composed of different parts. The cerebrum is the part of the dog's brain which performs functions such as learning.
Canine Internal Anatomy Chart Poster Laminated ubicaciondepersonas
Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.
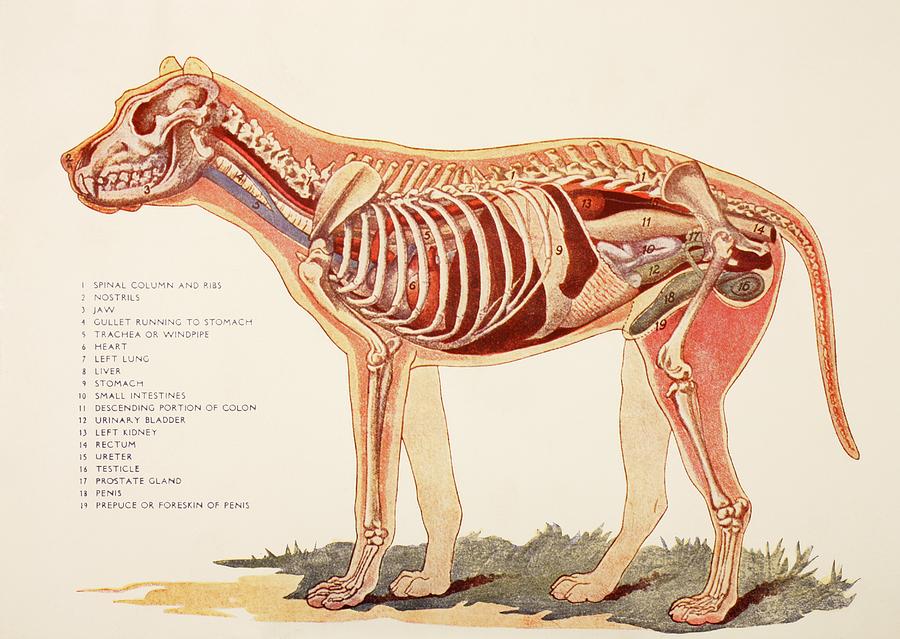
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh Pixels
A female dog's reproductive system has similar organs as a human's. The female dog anatomy external organ is the vulva, which opens to the vagina. A pregnant female dog's anatomy includes two ovaries, which produce eggs, the cervix, fallopian tubes, and the uterus. The uterus becomes the womb for her puppies during their gestation period.

dog anatomy Dog Care Training Grooming
Internal anatomy of a dog: carnivorous domestic mammal raised to perform various tasks for humans. Encephalon: seat of the intelluctual capacities of a gog. Spinal column: important part of the nervous system. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Spleen: hematopoiesis organ that produces lymphocytes.

Dog Anatomy Skeleton Animaltia
The internal organs of a dog include the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, stomach, intestines, and reproductive organs. These organs work together to keep the dog healthy and functioning properly. For example, the heart pumps blood throughout the body, while the kidneys filter waste products from the blood.
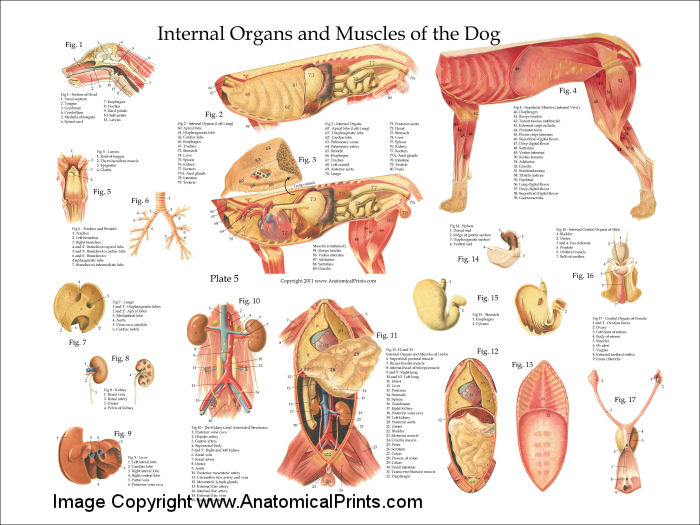
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster
The anatomy of the temporal bone and the ear is complex as this region concentrates a large number of bony, muscular, articular, vascular and nervous structures. The purpose of the current anatomy module is to describe the normal anatomy of the inner and middle ear of the dog as depicted using CT of the temporal bone. Material and methods